A comparison of the extent of energy price increases for consumers in the UK and France has attracted a lot of attention. The French government, in a presidential election year, has been quick to limit the extent of any increase for the consumer resulting from massive increases in wholesale prices following the recovery from the pandemic and, more recently, Putin’s invasion of Ukraine. In contrast in the UK the regulator, Ofgem, has set a very large increase in its price cap, which will be painful for all UK consumers from this Spring. (On the origins of the price cap see Giles Wilkes here.)
This in turn has reopened the debate between two different styles of relationship between the government and parts of the energy industry: nationalisation (EDF is largely owned by the French government) or regulation of privately owned companies (as in the UK). Many consumers will naturally see the ability of the government to directly limit energy prices as an advantage of the nationalisation model. In addition much has been made of the large increase in profits of many energy companies.
Any discussion on this issue can easily get bogged down in details. It is important to distinguish between energy supply (e.g. BP and Shell) and distribution (in the UK, dominated by the Big 6).The profits of the former are bound to rise when prices rise by far more than the cost of extracting energy. In the UK Ofgem regulates energy distribution, and when energy market prices rise this increases the costs these companies have to pay. This is the reason for the rise in Ofgem’s price cap, although that seems to be consistent with a recent large increase in profitsof the Big 6.
I want to abstract from this detail by thinking about a single (‘vertically integrated’) energy company that both supplies and distributes. The reason is that I want to focus on the distinction between prices and profits (or who benefits from higher prices). It is possible for the government to allow higher prices, but to tax the profits those higher prices bring to companies, and use these ‘windfall taxes’ to transfer money to consumers or for some other socially useful purpose. I want to argue here that this is exactly what should be happening right now.
Prices send out signals to both consumers and firms. Higher prices imply a commodity has seen a reduction in supply or a rise in demand, which encourages consumers to economise on using the commodity where they can. Equally the higher profits that tend to come with higher prices encourage firms to invest more to produce more of the commodity. The price signal is doing a useful job on both accounts.
However with energy, which at the margin is produced by burning carbon, it is also vital that we think about climate change, which is proceeding largely unchecked in an alarming way. Global warming is sometimes described by economists as the world’s biggest externality, by which they mean that the need to reduce climate change by consuming less carbon is not reflected in prices.
From the point of view of reducing carbon usage the higher prices for gas and electricity are beneficial. It is good to encourage less use of energy because that helps reduce climate change. By widening the gap between carbon based energy production and renewables, higher prices also encourage green energy supply. However higher energy prices also encourage additional extraction of oil and gas, and national governments typically don’t stop energy firms doing this (some may indeed encourage it).
It is in this context that we need to consider a recent proposalfrom the European Commission. They suggest member countries tax the profits energy companies made from recent energy price spikes and invest the revenue in renewable energy and energy-saving renovations. In doing this, the proposal suggests, EU governments would not be falling foul of EU rules.
The important point is that ‘excess’ profits are taxed, rather than what the money is spent on. Tax increases are not normally directly linked to how that money is spent (they are not hypothecated). In the UK more money is desperately needed by the poorest to help pay higher food and energy bills, and that is best provided by raising levels of Universal Credit. Whether the government does that from general taxation, some other means or from a windfall tax is incidental beyond media announcements.
The purpose of a windfall tax on energy companies is to ensure that the high profits made by these firms do not end up as paying for investment in non-green energy production, or as dividends or capital gains (from share buy-backs) to owners of the shares of those firms, but are directed to a more socially useful end.
What are the arguments against taxing the profits generated by high market prices? Let’s look at an FT editorialentitled “Windfall taxes on energy companies are a bad idea”. Among many paragraphs, the only substantive argument appears to be this:
“Stability is key to promoting both investment and spending — both of which drive economic growth. Predictable and constant regulations are identifiers of a society governed by the rule of law.”
Stability, the ultimate last resort of the conservative, is a non-argument in this case, as I would be quite happy to enshrine in the rule of law a tax schedule for these companies that taxes very high profits at a high marginal rate. Redirecting high profits to either green investment or higher benefits to the poor would also drive economic growth, with rather more drive than if the profits end up with shareholders. The editorial has all the hallmarks of some poor junior scribe being told to write something about why windfall taxes are a bad idea, and having to scrape the barrel to find any decent argument. I’m glad to see that Chris Giles, senior FT economics editor, has recently written in favour of windfall taxes on energy companies in the FT here.
One argument against nationalisation is that politicians come under huge pressure to keep prices low, as consumers (who are also voters) see the immediate benefit of lower prices, while the higher taxes, lower spending or whatever that is the counterpart of subsidizing energy is more opaque. A regulator is not under similar electoral pressure, and can ensure prices send appropriate signals. However such an argument against nationalisation can only be made if the government is prepared to implement windfall taxes on energy companies when their profits are very high, and that is something the UK government has not so far been prepared to do.
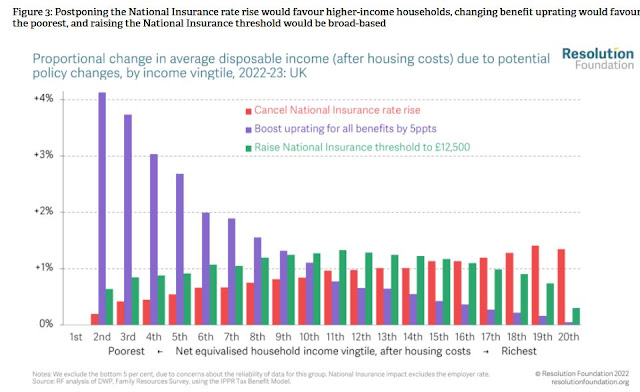
This argument is also central to the Chancellor’s Spring Statement tomorrow. The Resolution Foundation sets out some of his options here. A cut in fuel duty, though widely expected, just subsidises CO2 emissions at a significant cost to the public. Hardly surprising from successive Conservative Chancellors who keep promising to put up fuel duty and keep failing to do so, making nonsense of claims this is a green government. On other measures, Sunak should focus on a large uprating in universal benefit which provides most help to those who need it, as the Resolution Foundation shows.
But there are few votes for him in helping the poor, so that outcome seems less likely to happen.